Why You Need To Be Supplementing Glutamine Post-Training
How intense training compromises your gut and the glutamine protocol that fixes it
My interest in a compound or protocol usually emerges from of a problem — either my own, anyone I’m working with, or from DMs here on Substack/X. In the case of glutamine, it was my brother’s T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia diagnosis last year. Since this one hit close to home, my personal testing & research went deeper than usual.
The results were remarkable. Not just for my brother navigating chemotherapy, but for others dealing with everything from occasional indigestion to chronic gut inflammation to exercise-induced muscle soreness. And there’s good reason to believe the benefits extend well beyond these.
What we’re covering this week:
What is Glutamine?
How It Works
Benefits (as seen through the latest research)
Protocol Guide
Brands I Trust (& ones to avoid)
What is Glutamine?
As the most abundant free amino acid in the body, glutamine makes up ~60% of the total amino acid pool in skeletal muscle and is involved in over 100 metabolic pathways, acting as a nitrogen shuttle, energy substrate, & precursor for neurotransmitters and DNA building blocks. It’s classified as a conditionally essential amino acid meaning our body can synthesize enough glutamine endogenously (skeletal muscle, lungs, & liver) from other amino acids like glutamate & ammonia via the enzyme glutamine synthetase.1
However, during periods of high stress (i.e. intense training, illness, injury, or a major surgery) demand shoot ups while production can’t quite keep up.
How Glutamine Deficiencies Weaken Immune Function & Hinder Your Performance Recovery
Periods of prolonged or intense training deplete muscle glutamine levels by ~35% through a metabolic imbalance2. As skeletal muscle releases glutamine during exercise, uptake through the body accelerates in the liver (gluconeogenesis), kidneys (acid-base buffering), gut (barrier maintenance), & immune cells being activated.
This depletion is why we typically see elevated rates of immunosuppression among endurance athletes.3 Overtrained athletes with chronically low glutamine (greater than 10% below baseline) experience up to 6x higher upper respiratory infection rates due to drastic reductions in T-cell/B-cell proliferation, antibody production, & pathogen clearance capacity.
Not only is immune function weakened, but efficient muscle recovery is slowed. Since glutamine makes up ~50% of all intramuscular amino acids, we see greater strength losses via impaired glycogen resynthesis, increased low-grade inflammation, & inhibited muscle protein synthesis.
Mechanisms of Action
Intestinal Barrier Integrity
Glutamine serves as the main energy source for enterocytes → cells lining the small intestine renewing every 3–5 days. Through a process called glutaminolysis, enterocytes convert glutamine → glutamate (via glutaminase enzyme) → α-ketoglutarate, which feeds directly into the Krebs cycle for ATP production.
Glutamine fortifies tight junction proteins (i.e. zonulin & occludin) reducing intestinal permeability (”leaky gut”) & mitigating lipopolysaccharide (LPS) leakage from gram-negative bacteria - responsible for systemic inflammation. As a result, we get enhanced nutrient uptake, fewer GI issues, & sustained barrier integrity during high stress.
Immune Cell Proliferation & Function
Immune cells consume glutamine at rates 10 - 100x higher4 than other tissues when activated.
Two primary sub-mechanisms govern this function:
Rapid Cell Division: Glutamine supplies nitrogen for nucleotide synthesis (DNA/RNA building blocks), enabling T-cells to proliferate & produce the antibodies needed for recovery. Without adequate glutamine, immune cells can’t replicate efficiently.
Antioxidant Support: Glutamine serves as a precursor for glutathione (GSH) → our primary intracellular antioxidant. This helps in protecting immune cells from oxidative damage during pathogen elimination efforts.
Muscle Recovery & Metabolic Homeostasis
Skeletal muscle is our primary glutamine producer but intense training, fasting, or calorie deficits turn it into a net releaser, depleting stores. Glutamine attenuates muscle soreness by upregulating heat shock proteins (HSP70), reducing creatine kinase leakage, & lowering inflammation. While on the metabolic front, it increases insulin-independent glucose uptake in muscle cells (something we’ll account for in our protocol development later on).
Regardless of whether you have persisting issues with your gut post-training or not, there’s a good chance even low dosage glutamine can mitigate exercise-induced intestinal permeability.
Not convinced? Maybe every major human randomized controlled & clinical trial summarized & visualized from the last 3 decades will nudge you.
Health Benefits
Gut Health
Intestinal Permeability
Hond et al. (1999)5 demonstrated glutamine’s protective effect against NSAID-induced intestinal damage in 54 healthy volunteers. NSAIDs alone increased gut permeability to 1.69%, but supplementation with 21g/day of glutamine for 7 days reduced permeability by 37% to 1.06%.
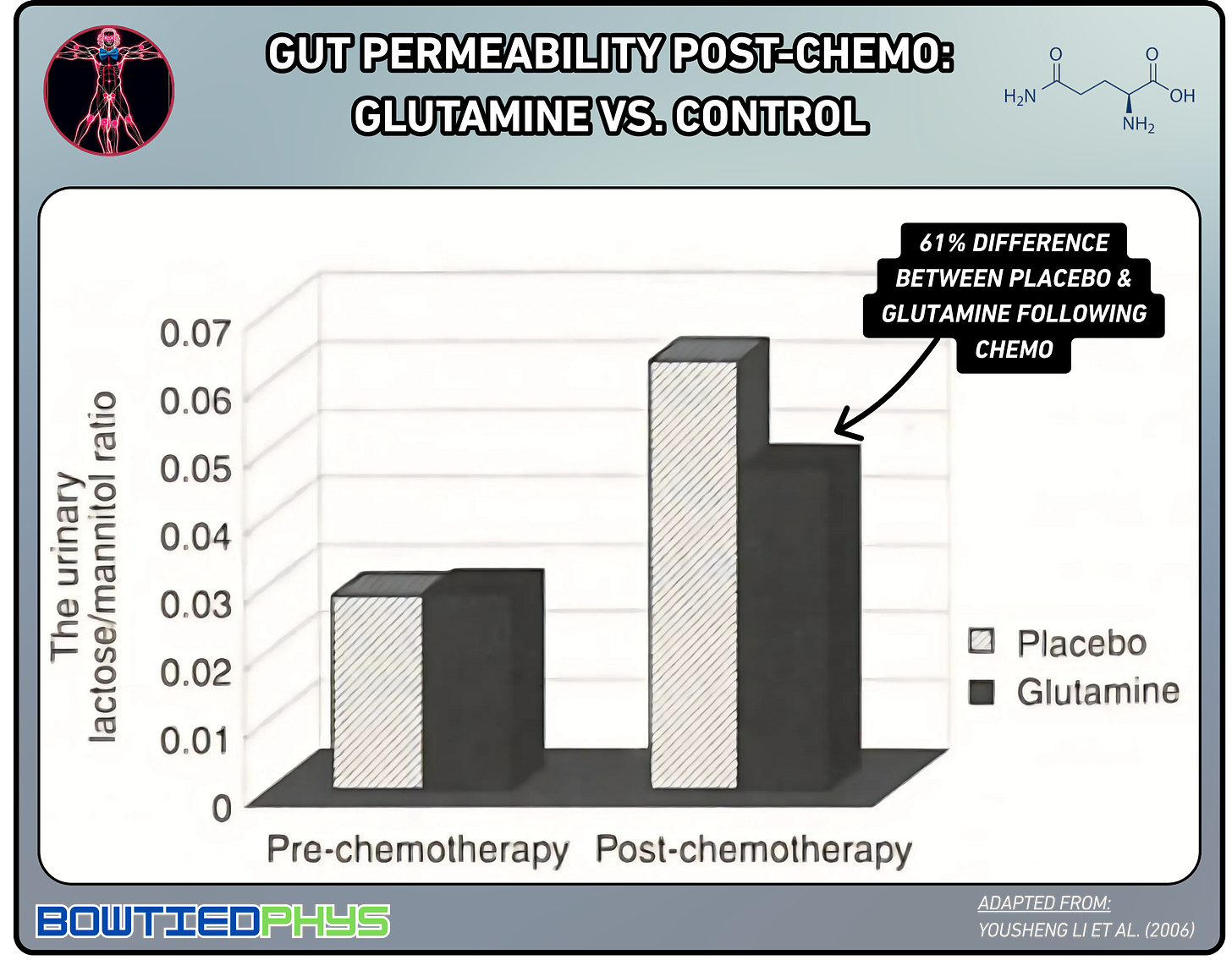
In this prospective randomized trial by Yousheng Li et al. (2006)6, 60 patients with breast cancer were assigned to receive either oral glutamine or placebo for at least 12 days alongside chemotherapy. The glutamine group showed a significantly lower lactulose-mannitol ratio post-chemotherapy → indicating reduced intestinal permeability.
Gut Inflammation
Peterson et al. (2007)7 conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial with 326 breast cancer patients experiencing oral mucositis during chemotherapy. Participants got either glutamine (Saforis) or placebo 3x daily. Glutamine significantly reduced moderate oral mucositis (grade ≥2) compared to placebo (38.7% vs. 49.7%) & dramatically decreased severe oral mucositis (grade ≥3) (1.2% vs. 6.7%).
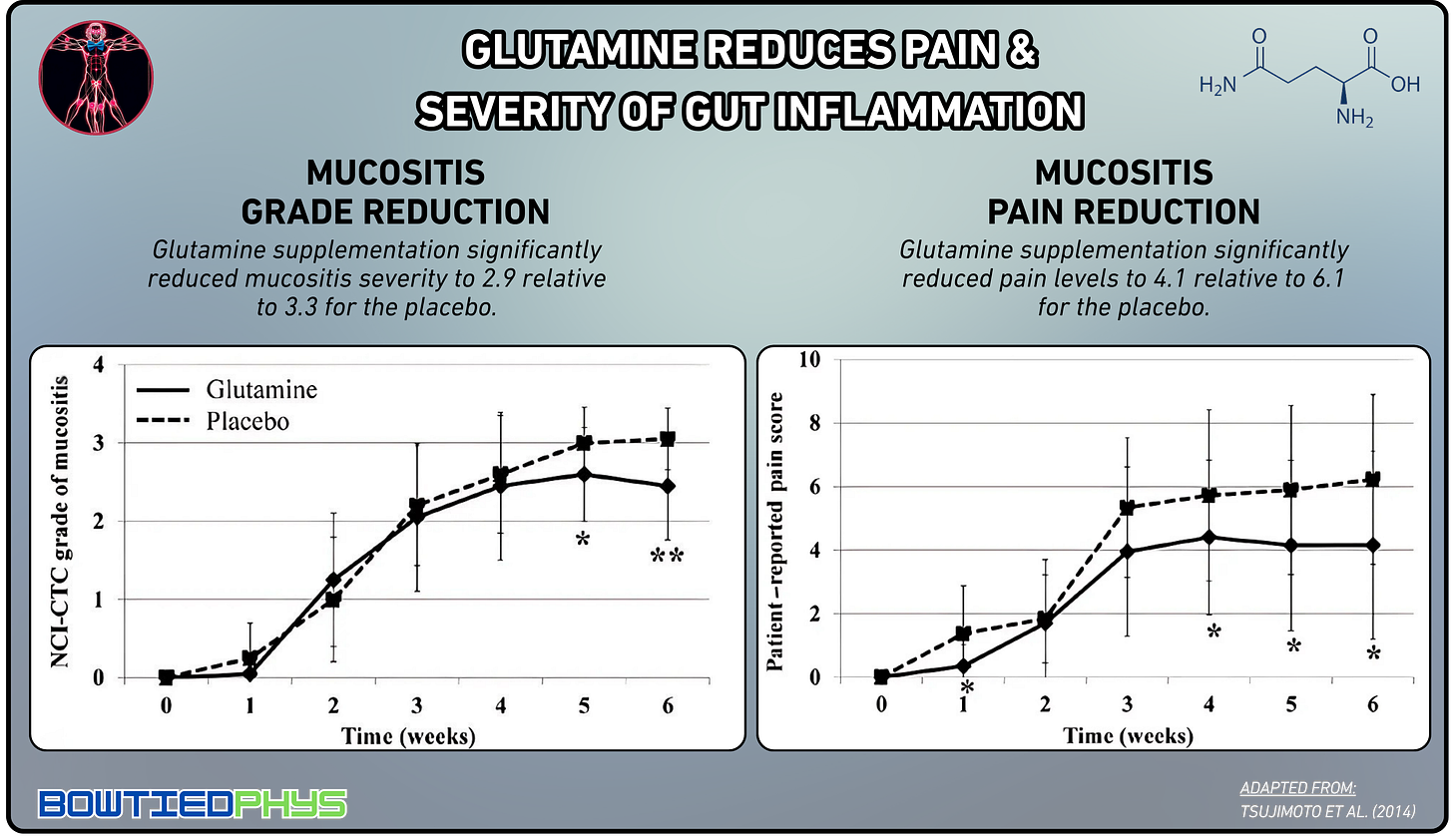
A study of 40 untreated patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer by Tsujimoto et al. (2014)8 reinforced these protective effects. Patients received either 10g of glutamine 3x daily or placebo alongside chemotherapy. Glutamine significantly reduced mucositis severity scores (2.9 vs. 3.3 for placebo) and decreased self-reported pain scores.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Zhou et al. (2019)9 randomized 106 adults with IBS & increased intestinal permeability to receive oral glutamine (5g 3x daily) or placebo for 8 weeks. 79.6% of glutamine participants achieved a significant ≥50-point reduction on the IBS Severity Scoring System (IBS-SS) compared to 5.8% in the placebo group.
The glutamine group also reduced daily bowel movement frequency & improved stool consistency.
Gut Microbiome Enhancement
Zambom de Souza et al. (2015)10 randomized 33 overweight/obese adults to receive either 30g daily of L-glutamine or placebo for 14 days in a double-blind study. The glutamine group demonstrated a significant reduction in the Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio → associated with obesity (0.57 vs. 0.85 at baseline) & decreased specific Firmicutes genera (Dialister, Dorea, Pseudobutyrivibrio, Veillonella), while the control group showed the opposite trend (1.12 vs. 0.91 at baseline).
Cardiometabolic Health
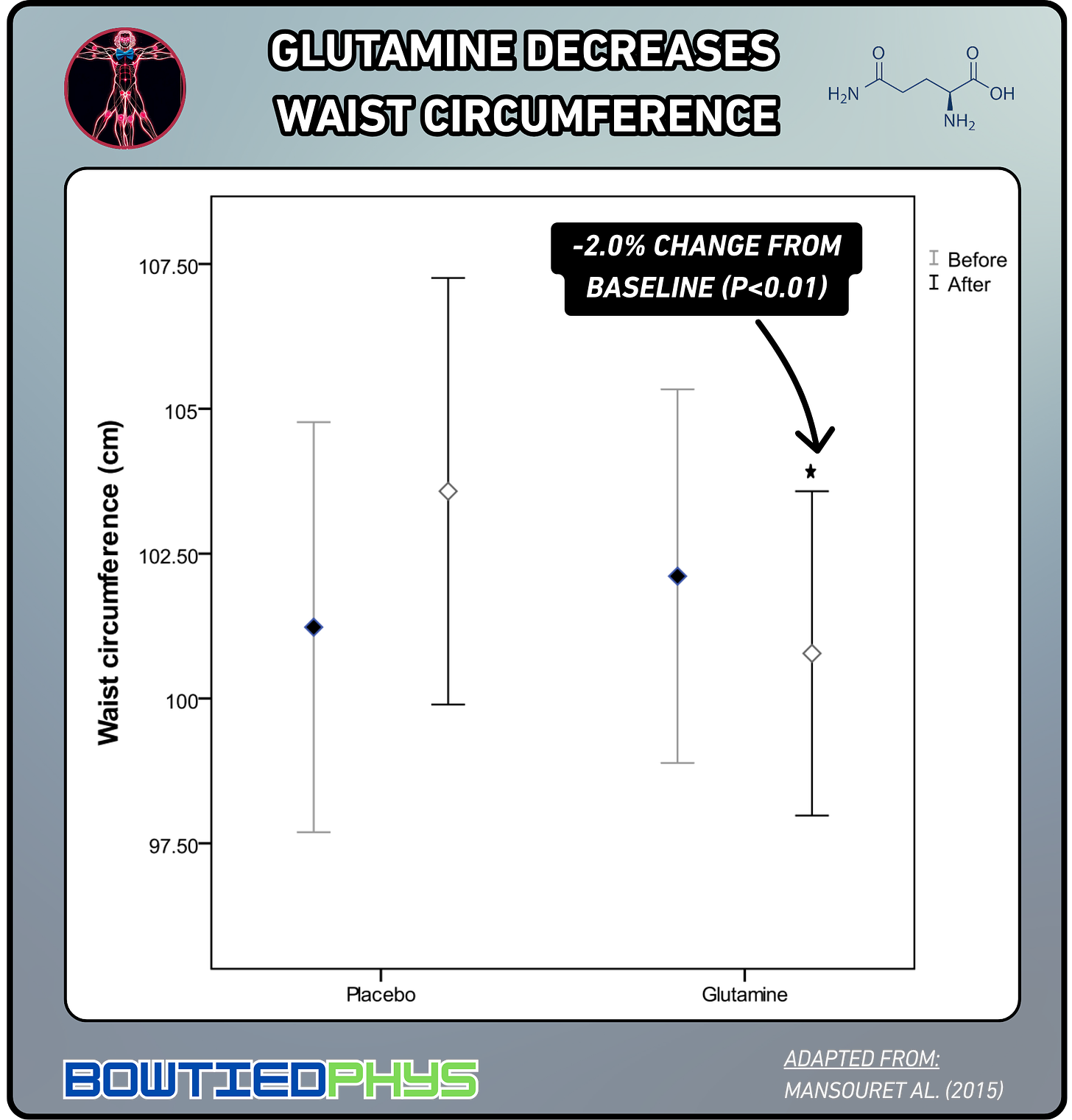
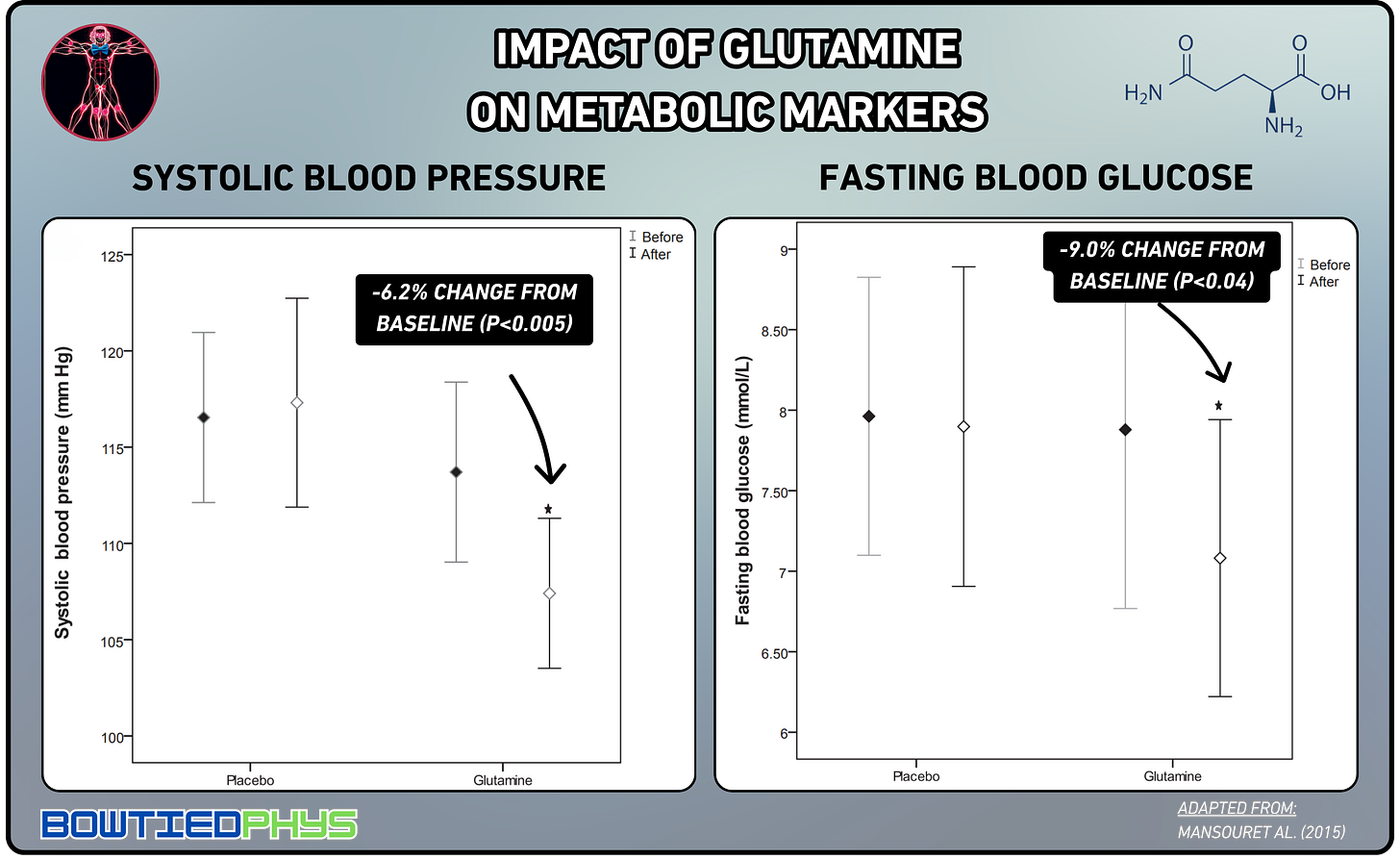
Mansour et al. (2015)11 randomized 66 patients with type 2 diabetes to receive either 30g daily of glutamine (10g three times daily) or placebo for 6 weeks in a double-blind trial. Glutamine supplementation significantly reduced waist circumference by 1cm (102.5cm to 101.5cm, a 2% decrease).
And also improved both systolic blood pressure & fasting blood glucose.
Atherosclerosis Risk Reduction
A 14-day RCT from Alipanah-Moghadam et al. (2022)12 studied 30 healthy males receiving either glutamine (0.3g/kg daily) or placebo for 14 days. Following exhaustive exercise, the glutamine group showed significantly lower leptin, cholesterol, oxidized LDL, IL-6, & oxidized LDL/HDL ratios compared to controls.
You can dial in your glutamine protocol all you want. But the truth is you’re flying blind if you don’t know what’s actually happening under the metabolic hood.
Your gut permeability. Your recovery markers. Your inflammatory load. By the time symptoms come up, you’re already months behind.
Most doctors are ordering blood work from 1990. Fasting glucose, basic lipids, maybe a CBC. But fasting insulin? ApoB? Lp(a)? CRP? The markers that actually matter for your long-term health? Rarely.
That’s why I use Superpower.
100+ biomarkers. 3,000 labs to test in. 24/7 unlimited access to medical practitioners.
All at just $17/month.
Test. Don’t guess.
Exercise & Sports Performance
Muscle Damage
In this crossover trial by Córdova-Martínez et al. (2021)13, 12 professional basketball players received either 6 g/day of glutamine or placebo for 40 days. Glutamine significantly reduced markers of muscle damage (aspartate transaminase, creatine kinase, & myoglobin). The glutamine group also lowered adrenocorticotropic hormone & stabilized cortisol levels relative to placebo.
Strength Recovery & Soreness
Legault et al. (2015)14 examined recovery in 16 healthy subjects following intense eccentric knee exercise (8 sets of 10 reps at 125% maximum concentric force). Subjects got either L-glutamine or an isoenergetic placebo daily for 72 hours. Glutamine preserved greater peak torque at 180°/sec immediately post-exercise (71% vs. 66%) & at 72 hours (91% vs. 86%). Muscle soreness was also significantly lower in the glutamine group at 24 hours, 48 hours, & 72 hours post-exercise.
Amirato et al. (2021)15 showed that glutamine significantly improved knee torque & enhanced glycemic control (lower D-fructosamine) over a 30-day period. Both physically active & sedentary glutamine groups demonstrated decreased oxidative stress markers (TBARS).
Exercise-Induced Gut Permeability
Pugh et al. (2017)16 studied 10 recreationally active males performing a 60-minute treadmill run at 70% VO2max. The athletes consumed glutamine at 0.25, 0.5, or 0.9 g/kg fat-free mass or placebo 2 hours pre-exercise. Glutamine dose-dependently reduced gastrointestinal permeability (lactulose:rhamnose ratio: -0.023, -0.019, & -0.034 respectively) relative to placebo.
In a trial by Zuhl et al. (2014)17, 8 subjects completed a 60-minute treadmill run after 7 days of glutamine or placebo supplementation. Glutamine significantly reduced exercise-induced intestinal permeability vs. placebo (0.0272 vs. 0.0604) & decreased inflammatory markers post-exercise.
Immunity
In this trial by Castell and Newsholme (1997)18, glutamine supplementation reduced the incidence of upper respiratory tract infections (URTI) compared to placebo and increased the T-helper/T-suppressor cell ratio. Plasma glutamine levels notably dropped by ~20% one hour post-marathon, with a marked post-exercise increase in white blood cells followed by a lymphocyte decrease.
In another randomized, placebo-controlled trial from Song et al. (2015)19, 24 athletes undergoing heavy training loads for 6 weeks received either 10 g/day glutamine or placebo starting 3 weeks after initial testing. Glutamine supplementation significantly improved multiple immunity markers: CD4⁺/CD8⁺ T cell ratio, reduced CD8⁺ T cell percentages, & enhanced natural killer (NK) cell activity.
Inflammation
Skin Inflammation
In this trial from Lopez-Vaquero et al. (2017)20, 50 head/neck cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy received either 10g L-glutamine 3x daily or placebo for 6 weeks. Glutamine significantly reduced both the incidence & severity of facial dermatitis compared to placebo.
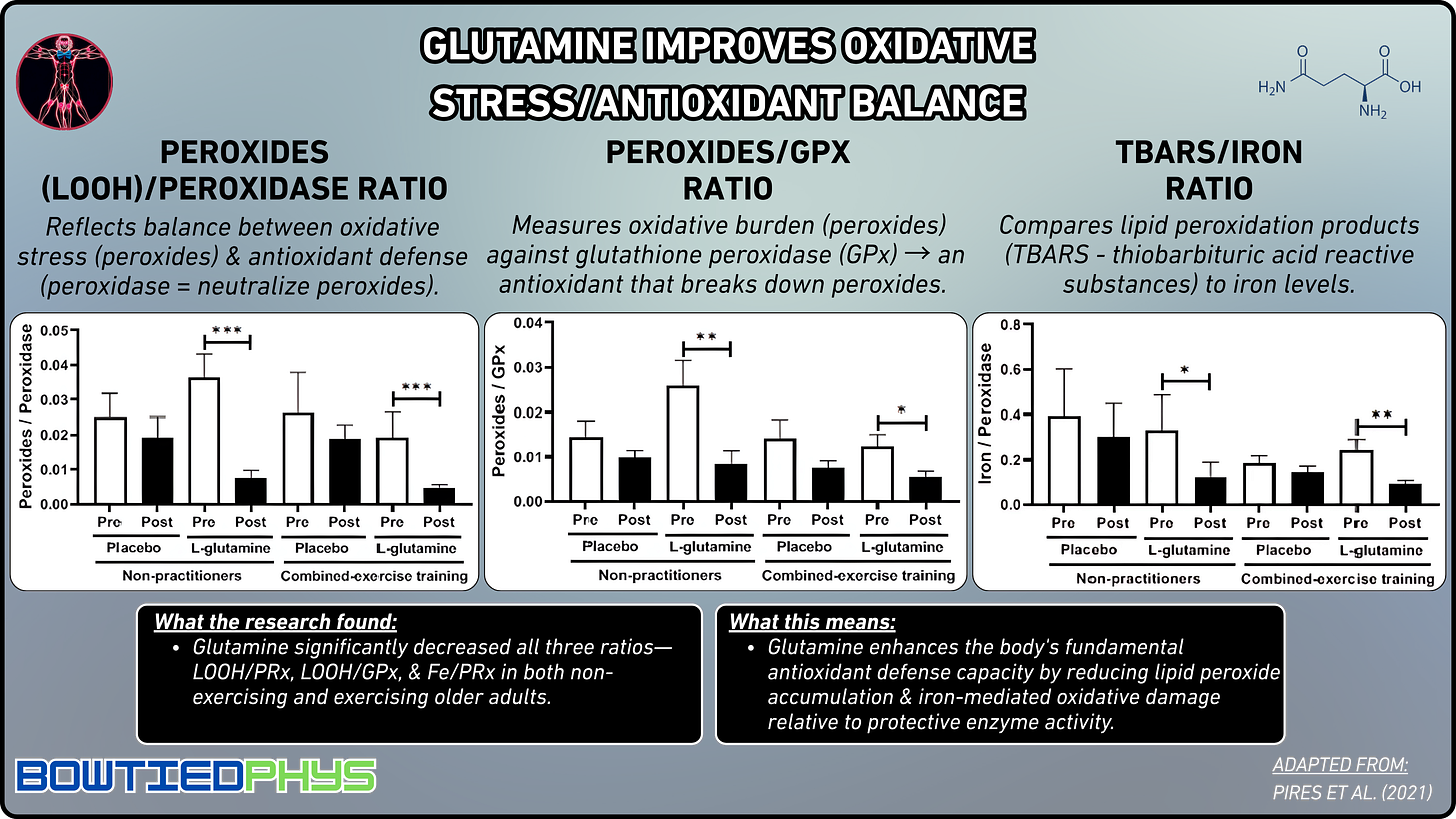
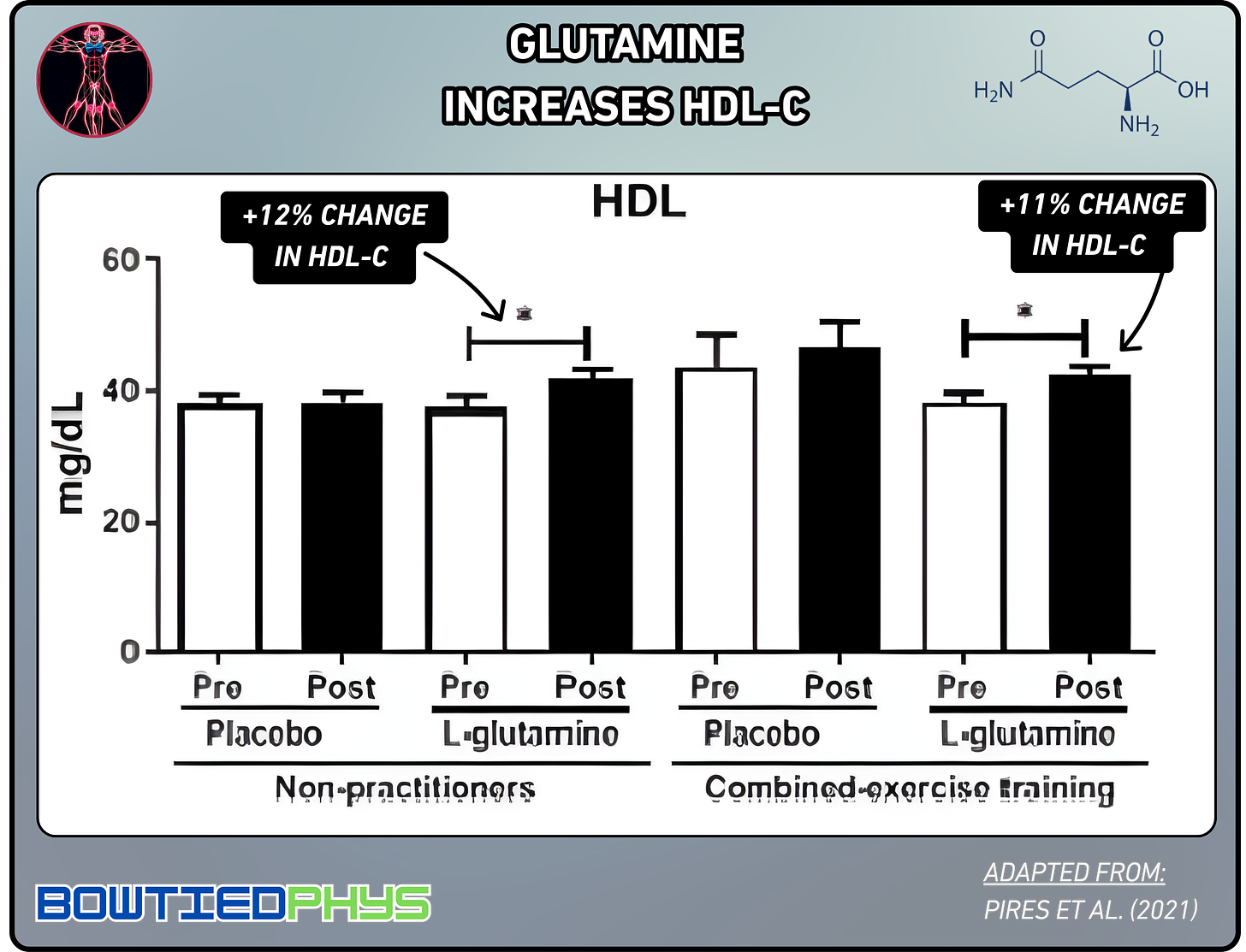
Redox Balance
In this randomized, placebo-controlled trial by Pires et al. (2021)21, 83 elderly individuals (51 exercising, 32 sedentary) took either L-glutamine (0.3g/kg/day) or placebo for 30 days. Glutamine significantly increased HDL-C & antioxidant enzymes in both groups.
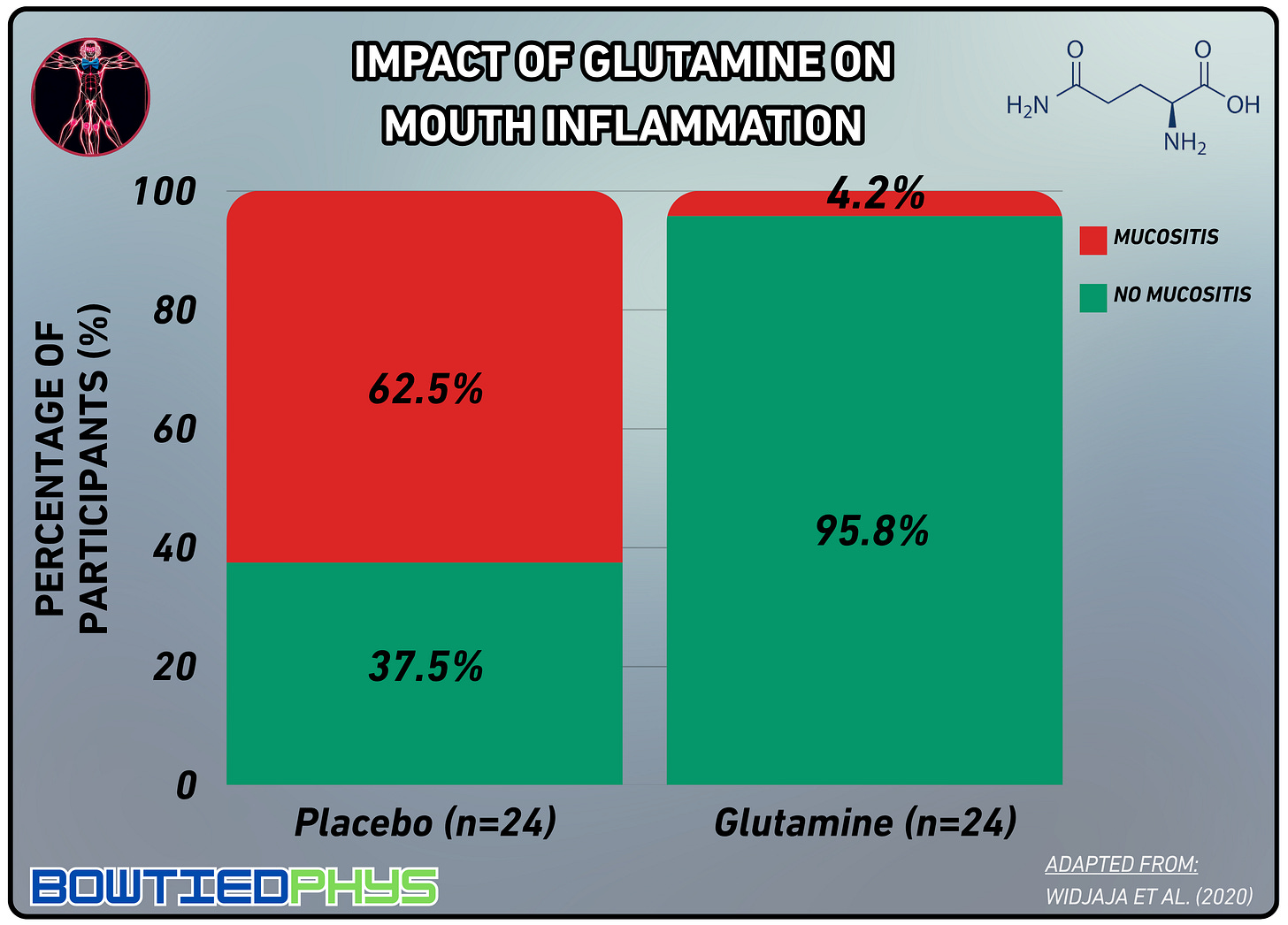
Mucositis
48 children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia received either oral glutamine (400mg/kg/day) or placebo during chemotherapy in a trial by Widjaja et al. (2020)22 Glutamine significantly reduced oral mucositis incidence (4.2% vs. 62.5%), shortened hospital stays (8 vs. 12 days), & lowered daily hospital costs ($40 vs. $48).
Markers
In a trial by Nava et al. (2019)23, 11 young adults completed simulated wildland firefighting tasks in hot conditions over 2 consecutive days. Glutamine significantly reduced GI damage (via plasma I-FABP), subjective fatigue, & perceived exertion relative to placebo, while increasing heat shock protein 70 & IκBα levels, indicating enhanced GI barrier protection and reduced inflammation.
Immune Health
Improvement of Critical Illness Outcomes
In a double-blind trial by Griffiths (1997)24, 84 critically ill patients with multiple organ failure received either glutamine-supplemented parenteral nutrition (25g/day) or placebo. Glutamine significantly improved 6-month survival (57% vs. 33%) & reduced ICU costs per survivor by 50%.
Adjunct Cancer Treatment
Okur et al. (2006) conducted a randomized crossover trial in 21 pediatric cancer patients receiving chemotherapy, comparing courses with & without oral glutamine (0.65g/kg/day for 5 days). Glutamine supplementation preserved nutritional & immune markers → significantly increasing prealbumin, transferrin, & complement proteins C3 and C4, while reducing antibiotic use.
Hormonal Health
In this randomized, placebo-controlled trial by Lu et al. (2024)25, 21 combat-sport athletes received either 0.3g/kg body weight of L-glutamine or placebo daily for 3 weeks following intense training. The glutamine group demonstrated significantly increased salivary IgA & nitric oxide levels, reduced upper respiratory tract infections, & improved testosterone-to-cortisol ratio compared to placebo.