Supplement Spotlight #5: Taurine
22 research papers & 6 primary mechanisms reviewed on the cardiometabolic amino acid elixir
Welcome back loyal subscribers - we’re delivering another round of the supplement spotlight series.
This week we’re featuring an increasingly popular utility tool of supplements - TAURINE.
You’ll get the sense quickly why this often forgotten amino acid is becoming one of the most popular supplements on the market today. Red Bull was ahead of the curve.

What we’ll cover:
What is taurine?
How it works
Benefits (as seen through the latest research)
Protocols
Brands I trust
What is Taurine?
Taurine (C₂H₇NO₃S) is a sulfur-containing β-amino acid endogenously synthesized via the cysteine sulfinic acid pathway in the liver & brain. Taurine is unlike typical amino acids we see in complete proteins in that it lacks a carboxyl group (COOH). Its unique chemical structure enables it to exhibit a diverse set of biochemical interactions we’ll discuss next.

Mechanisms of Action
As always, if you’re less interested in how taurine functions, skip down to the next section - “Health Benefits”. But I’ll keep this section to a cursory overview of the main mechanisms regarding how taurine acts on the body.
Cellular Protection
Taurine functions as both a direct & indirect antioxidant mitigating oxidative stress:
Scavenging reactive oxygen species: Neutralizes hydroxyl radicals (OH) & hypochlorous acid (HOCl)
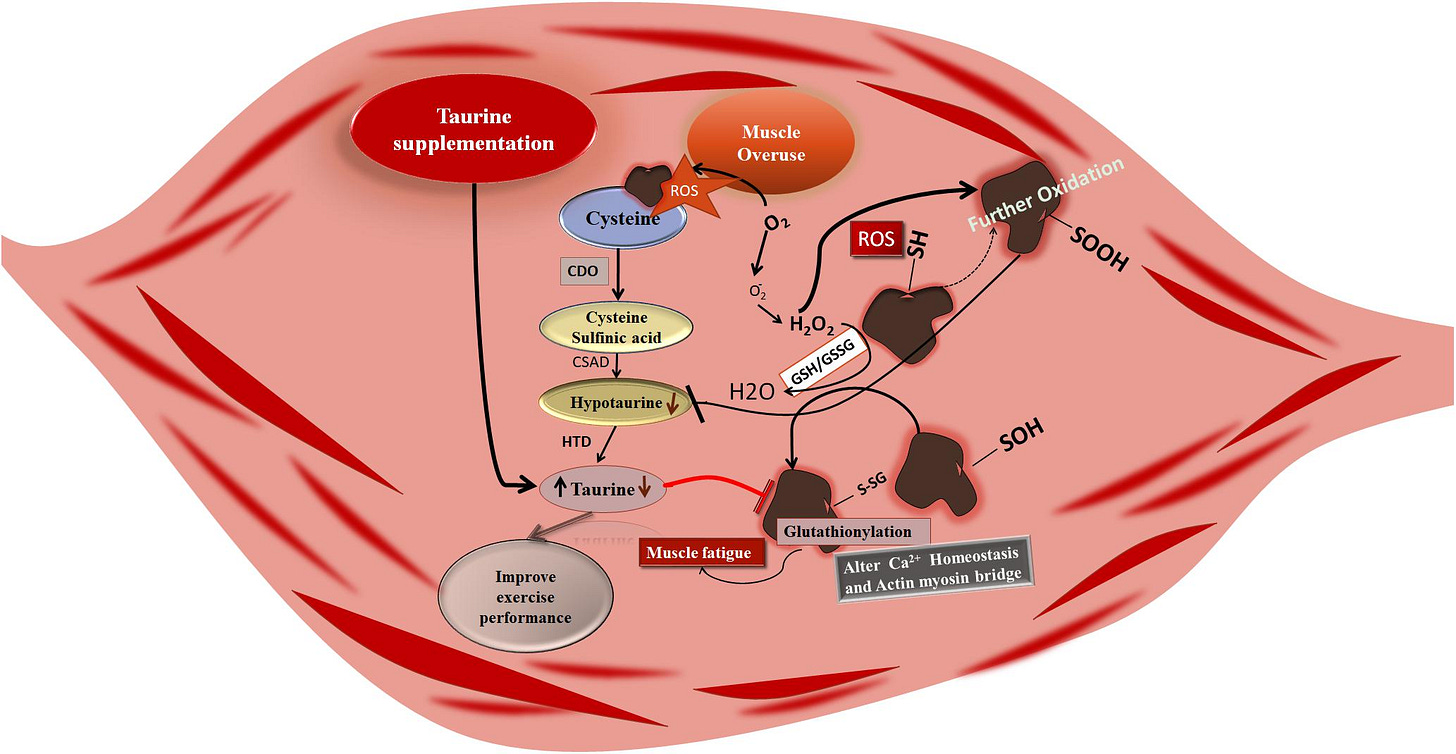
Taurine’s free radical scavenging mechanisms (Source) Enhancing endogenous antioxidant systems: Upregulates glutathione (GSH) synthesis & activity of enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), & glutathione peroxidase (GPx)
Metabolic Regulation
Improving both glucose & lipid homeostasis, taurine serves as a metabolic modulator:
Sensitizing insulin: Promotes the movement of GLUT4 (glucose transporters) to the cell surface allowing more glucose to enter cells

Taurine’s regulation of glucose uptake in skeletal muscle (Source) Increasing mitochondrial biogenesis: Activates AMPK & PGC-1α increasing fat oxidation & energy expenditure
Cardiovascular Health
Taurine acts as a cardioprotective lever:
Regulating blood pressure: Enhances endothelial nitric oxide (NO) production & inhibits angiotensin II signaling → promotes vasodilation
Modulating ion channels: Regulates Na/K-ATPase (enzyme moving Na & K across cell membranes) and potassium channels maintaining electrophysiological stability
Enhancing lipid metabolism: Joins with bile acids to enhance cholesterol excretion lowering serum LDL-C & triglycerides
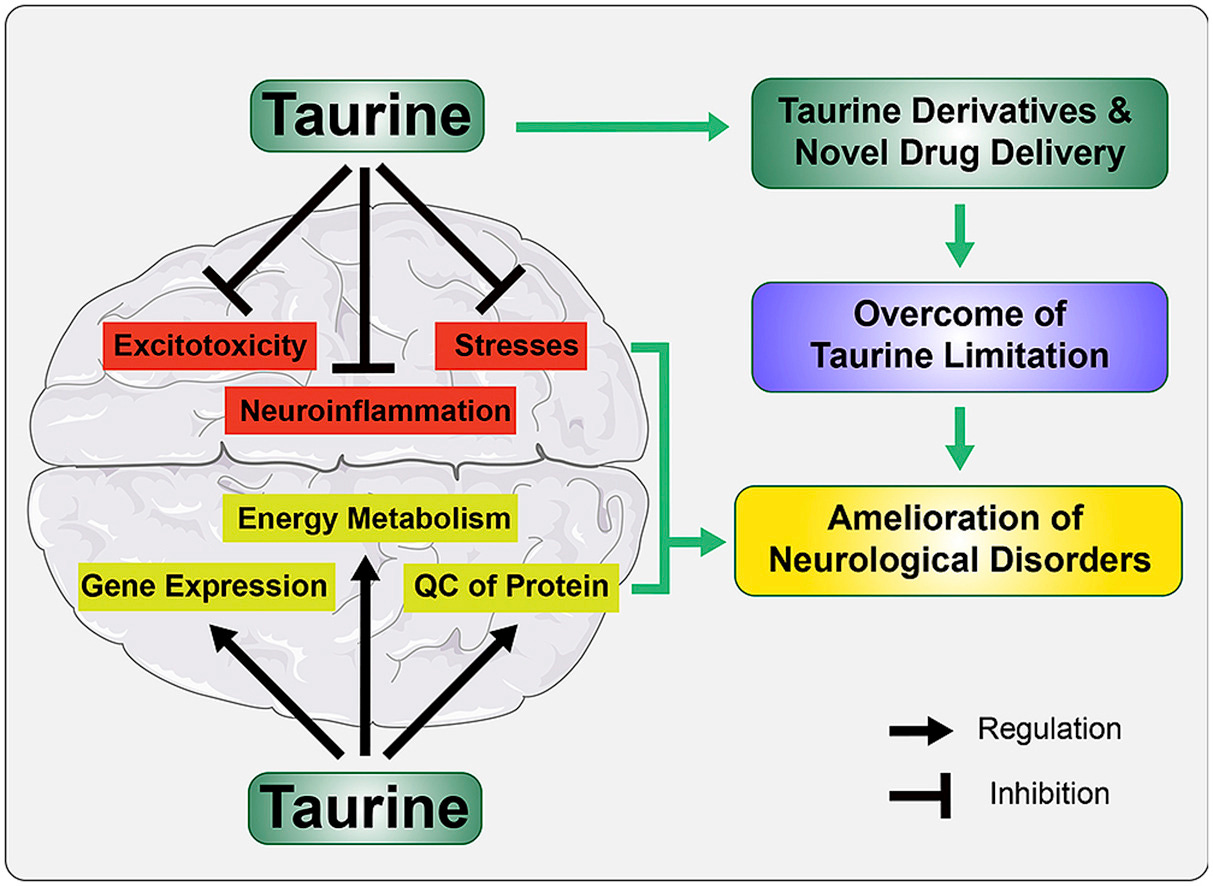
Neuroprotection
Taurine prevents excitotoxicity & neurodegeneration:
Modulating GABA/glutamate balance: Blocks NMDA receptor-mediated calcium ion influx & serves as a GABA agonist
Upregulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): Decreases neuroinflammation & amyloid-β aggregation via NF-κB (pro-inflammatory) suppression
Muscular Function
As we’ll see in the next section, taurine boasts significant impacts on cardiometabolic & skeletal muscle performance:
Improving calcium uptake: Enhances the release of calcium from muscle storage sites & increases calcium reuptake following muscle contraction
Delaying muscle fatigue: Mitigates exercise-induced oxidative damage lowering lactic acid buildup
Longevity
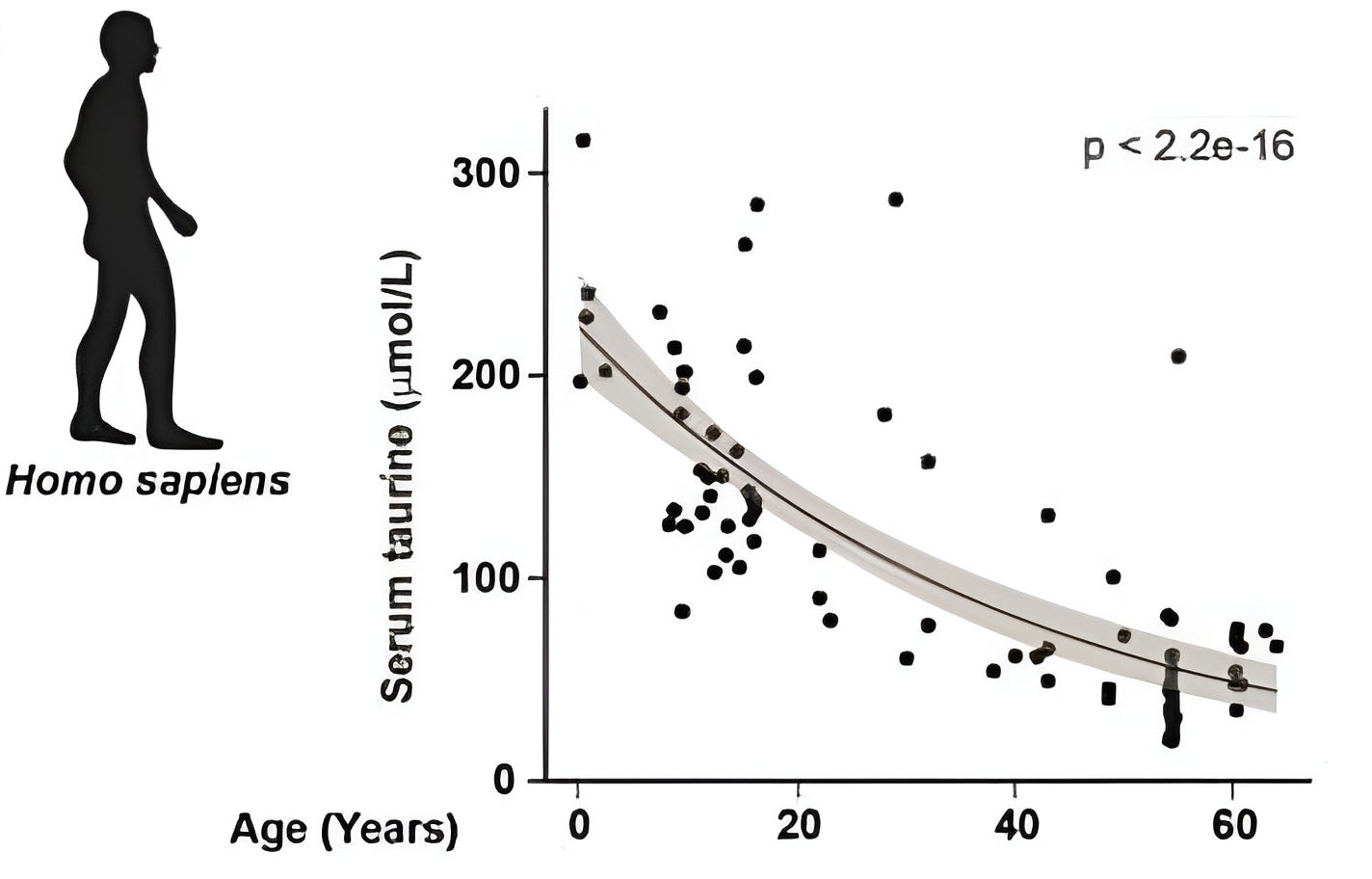
Within the last two years, taurine has gained most of its attention in the longevity space as a potential healthspan optimization compound:
Enhancing mitochondrial efficiency: Improves ATP production in cells reducing the amount of ROS generation
Preserving telomere length: Protects DNA integrity by maintaining the protective caps on chromosomes (telomeres) & decreases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokine production
Health Benefits
Though taurine research has been ongoing since the late 1980s, it’s only recently had a surge in popularity due to its compelling potential as a longevity component.
Outlined below are the 22 most compelling research papers supporting taurine’s efficacy across a wide range of use cases.
Metabolic Health
A well-conducted meta-analysis of 25 RCTs from May 2024 regarding taurine's impact on 1,024 subjects noted significant reductions in multiple metabolic biomarkers:
Systolic blood pressure (-4.0 mm Hg)
Diastolic blood pressure (-1.5 mm Hg)
Fasting blood glucose (-5.9 mg/dL)
Triglycerides (-18.3 mg/dL)
Let's take a look at a couple powerful ones individually within the meta-analysis.
40 middle-aged females with type 2 diabetes were divided into four groups: training + taurine (TT), training + placebo (TP), taurine only (T), & control (C). were administered 500 mg 2x daily for 8 weeks. Relative to other groups, the training + taurine group demonstrated significantly greater reductions in:
Fasting blood sugar
Insulin resistance
Triglycerides
HbA1c
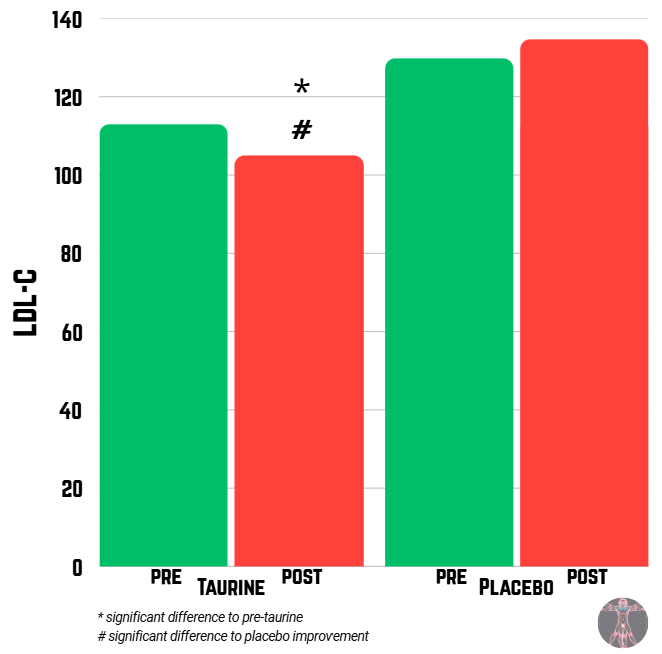
LDL-C
A similar 8-week clinical trial divided 45 type 2 diabetics into taurine (23 subjects) & placebo (22 subjects) groups. The taurine group - consuming 3 g daily for 8 weeks - saw significant improvements in multiple metabolic biomarkers:
Fasting blood glucose
Insulin resistance
LDL-C
Irisin Levels
Irisin is an endogenous hormone produced by muscle & fat tissue playing a vital role in the regulation of energy metabolism. Acute rises in irisin indicate enhanced metabolic adaptation, activated thermogenesis (i.e. browning of white fat), & improved glucose metabolism.
22 obese women were divided into a control (14 subjects) receiving a placebo & exercise and treatment group receiving 3 g taurine & exercise (8 subjects). Only the taurine group showed a significant increase in irisin levels demonstrating that taurine supplementation enhances the exercise-induced release of irisin.
Taurine is a metabolic powerhouse tool. But an area where it shines to an even greater extent? Cardiovascular health.