Supplement Spotlight #4: Nigella Sativa
Don't take all seed oils off the table
Welcome back loyal subscribers - we’re delivering another round of the supplement spotlight series this week.
One of my favorite spices with a rich history dating back thousands of years: black seed oil (Nigella sativa).
When I first entered into the health space years ago, it seemed too good to be true. I ordered some from a popular brand on Amazon. Saw little to no effect at the common clinical dosages. After two more attempts, I finally landed on a product where I was blown away by the benefits both by feel & via metabolic biomarkers. We’ll get to choosing the right product later.
What we’ll cover:
What is Nigella sativa?
How it works
Benefits (as seen through the latest research)
Protocols
Choosing the right product
Brands I trust
What is Nigella sativa?
Nigella sativa, also referred to as black cumin or black seed oil, dates back thousands of years across multiple ancient cultures. It’s one of the most studied herbs to date traditionally cultivated in the Middle East, Western Asia, & Mediterranean region.
Its story began in ancient Egypt more than 3,000 years ago. Archaeologists discovered its presence in King Tutankhamun’s tomb symbolling protection in the afterlife. Ancient Egyptian records also showed it was a critical part of many dishes. Even Queen Nefertiti incorporated it as a part of her daily protocol. (Protocols run deep)
In Islamic medicine, Nigella sativa possesses immense value. The central figure of Islam, the Prophet Muhammed, regarded it as “a cure for every disease except death” eventually earning it the name of “The Blessed Seed” among Muslims.
Similarly, Greek physicians like Hippocrates & Dioscorides documented the therapeutic use of black seeds for digestive disorders, liver disease, & headaches.
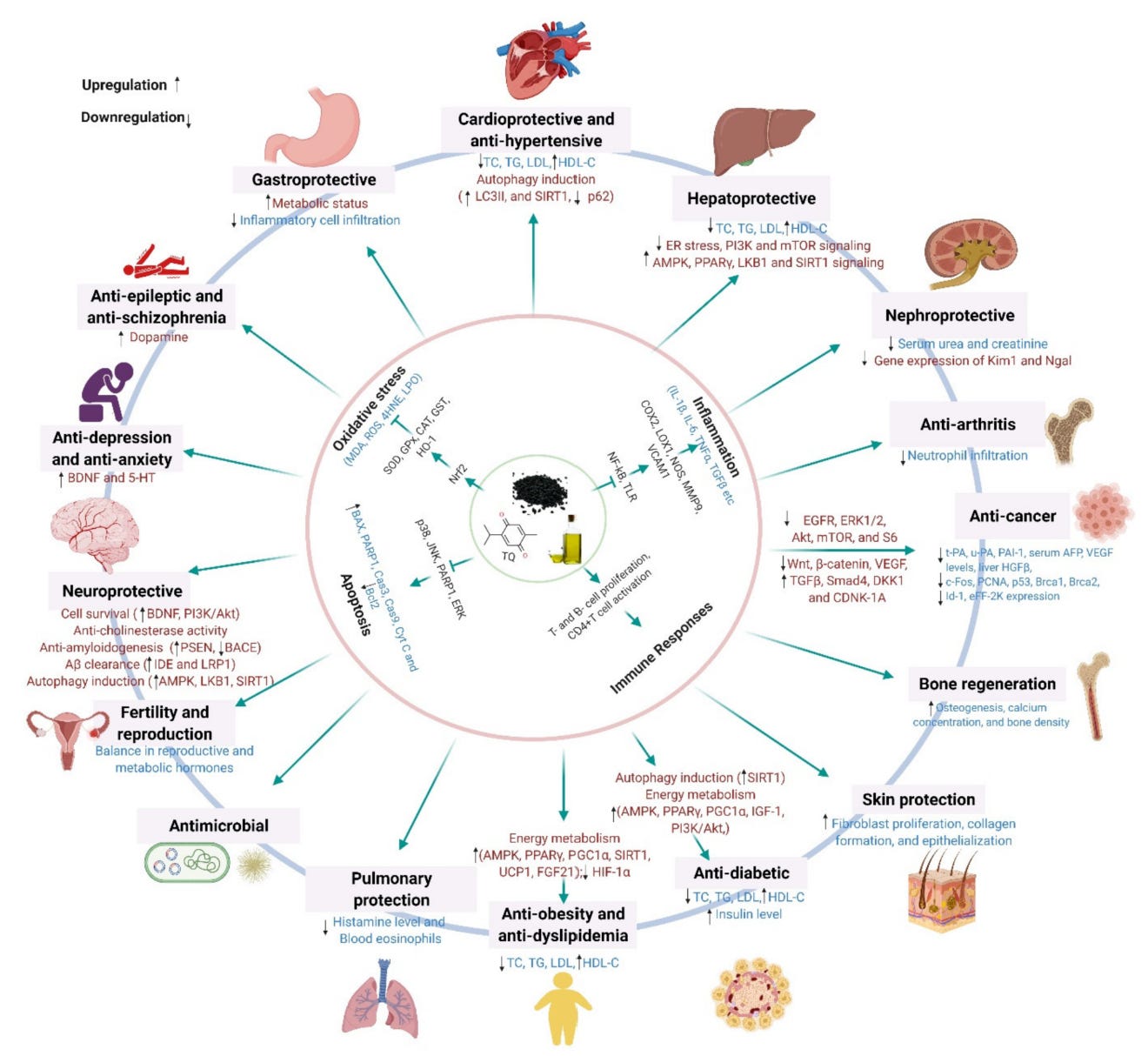
As for the chemical composition, Nigella sativa is largely made up of fixed oil & volatile oil (bioactive) components with a trace amount of minerals (calcium, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium) & polyphenols. Its fixed oil composition is broken down into unsaturated fatty acids (85%) and saturated fatty acids (15%), while its volatile oil content is comprised of more than 30 compounds. Thymoquinone - the main volatile compound - consists of ~20% of the bioactive compound makeup and drives a majority of Nigella sativa’s robust set of biological actions.
What makes black seed oil black is its high density of melanin - the same substance in human skin giving us our skin pigment & cellular protection from excessive UV radiation. Interestingly enough, we’ll get into some use cases for our skin later.
A $23M market today, black seed oil is expected to further that growth to a ~$43M market by 2033.
Mechanisms of Action
If you’re less interested in how Nigella sativa functions, skip down to the next section - “Health Benefits”. I’ll keep this section to a cursory overview of the main mechanisms of how it acts on our body.
There’s a reason pharmaceutical companies & academic institutions are attempting to patent thymoquinone and its derivatives. We’ll cover the primary mechanisms making Nigella sativa the powerful herb it is:
Immune modulating → Thymoquinone regulates key signaling pathways (NF-κB & STAT3), which control the production of inflammatory cytokines. This regulation prevents excessive inflammation while maintaining normal immune responses. Thymoquinone also helps balance T-helper cell responses (Th1/Th2) - responsible for determining which immune “strategy” to employ. Nigella sativa also enhances natural killer cell activity ensuring appropriate immune responses without overreaction.
Antioxidant → One of Nigella sativa’s most potent mechanisms. Thymoquinone acts through direct free radical scavenging donating electrons to neutralize these harmful free radicals. Simultaneously, it activates the body's internal antioxidant defense systems increasing production of glutathione & other antioxidant enzymes (i.e. superoxide dismutase, catalase). Thymoquinone also prevents lipid peroxidation in cell membranes inhibiting oxidative damage before it sparks.
Anti-inflammatory → The NF-κB pathway acts like a master switch controlling the production of inflammatory molecules in cells. Thymoquinone modulates this pathway reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (i.e. TNF-α, IL-1β, & IL-6) and supporting anti-inflammatory cytokines (i.e. IL-10).
Neuroprotective → What bolsters Nigella sativa’s brain protecting attributes is thymoquinone’s ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. Once in the brain, it protects neurons by regulating glutamate receptors & calcium channels preventing excitotoxic damage caused by excessive neurotransmitter activity. It also modulates central nervous system immune cells to reduce brain inflammation & increase brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels enhancing brain plasticity.
Cardioprotective → Given Nigella sativa’s strong antioxidant capability, reductions in reactive oxygen species contributes to less degradation of nitric oxide and therefore improved endothelial function & blood pressure reduction. It also inhibits the key enzyme involved in cholesterol biosynthesis - HMG-CoA reductase - modulating lipid metabolism.
Health Benefits
Metabolic Health
Glycemic Control
An RCT conducted on 43 T2 diabetes patients showed 1 g of BSO significantly improved various cardiometabolic risk factors compared to placebo:
HbA1C had a relative reduction of 8.9% from 7.9% to 7.2% (absolute drop of 0.7%).
Fasting blood sugar reduced 12% from 190 to 167 mg/dL.
Triglycerides dropped 11% from 156 to 139 mg/dL.
LDL-C decreased 14% from 114 to 98 mg/dL.
Blood Pressure
In a clinical trial of 114 subjects, T2 diabetics receiving 2 g daily for one year experienced significant decreases in diastolic & mean arterial blood pressure at the conclusion of month 12.

Cardiovascular Health
Lipids
Across 88 subjects with elevated lipid levels, 2 g daily of BSO over a 4-week period resulted in significant decreases in LDL cholesterol (7.6%) & triglycerides (16.7%).
Atherosclerotic Conditions
In an 8-week placebo-controlled RCT, 2 g of BSO was administered to the treatment group daily. Relative to the placebo group, the treatment group showed significant declines in the following endothelial & atherogenic indices:
Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 → protein expressed on the surface of blood vessel walls leading to atherosclerosis
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 → protein involved in cell-to-cell binding & a biomarker for vascular inflammation
Malondialdehyde → byproduct of lipid peroxidation & biomarker for oxidative stress levels
These improvements indicate BSO as an effective therapeutic agent against coronary artery disease.
Skin Health
Acne
BSO has been demonstrated as a potent intervention mechanism for acne. Results of this trial indicated significant reductions across three different acne lesions - comedones, papules, & pustules - as well as a Investigator’s Global Assessment of the patient’s skin.
At the conclusion of the 8-week trial, the following results were reported:
Comedones
BSO = 83.2% reduction
Placebo = 23.4% reduction
Papules
BSO = 79.4% reduction
Placebo = 11.3% reduction
Pustules
BSO = 73.1% reduction
Placebo = 6.2% reduction
IGA score
BSO = 78% reduction
Placebo = 3.3% reduction